Stay updated
News & Insightstitle: "example kaggle salt" notebookName: "example_kaggle_salt.ipynb"
Using Albumentations for a semantic segmentation task
We will use images and data from the TGS Salt Identification Challenge.
Import the required libraries
import albumentations as A
import cv2
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
Define a function to visualize images and masks
def visualize(image, mask, original_image=None, original_mask=None):
fontsize = 18
if original_image is None and original_mask is None:
_, ax = plt.subplots(2, 1, figsize=(8, 8))
ax[0].imshow(image)
ax[1].imshow(mask)
else:
_, ax = plt.subplots(2, 2, figsize=(8, 8))
ax[0, 0].imshow(original_image)
ax[0, 0].set_title("Original image", fontsize=fontsize)
ax[1, 0].imshow(original_mask)
ax[1, 0].set_title("Original mask", fontsize=fontsize)
ax[0, 1].imshow(image)
ax[0, 1].set_title("Transformed image", fontsize=fontsize)
ax[1, 1].imshow(mask)
ax[1, 1].set_title("Transformed mask", fontsize=fontsize)
Read an image and its mask from the disk
image = cv2.imread("images/kaggle_salt/0fea4b5049_image.png")
mask = cv2.imread("images/kaggle_salt/0fea4b5049.png", cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
Original image
print(image.shape, mask.shape)
(101, 101, 3) (101, 101)
original_height, original_width = image.shape[:2]
visualize(image, mask)
No code provided
No code providedPadding
UNet type architecture requires input image size be divisible by , where is the number of maxpooling layers. In the vanilla UNet , we need to pad input images to the closest divisible by number, which is 128. This operation may be performed using PadIfNeeded transformation. It pads both the image and the mask on all four sides. Padding type (zero, constant, reflection) may be specified. The default padding is reflection padding.
aug = A.PadIfNeeded(min_height=128, min_width=128, p=1)
augmented = aug(image=image, mask=mask)
image_padded = augmented["image"]
mask_padded = augmented["mask"]
print(image_padded.shape, mask_padded.shape)
visualize(image_padded, mask_padded, original_image=image, original_mask=mask)
(128, 128, 3) (128, 128)
No code provided
No code providedCenterCrop and Crop
To get to the original image and mask from the padded version, we may use CenterCrop or Crop transformations.
aug = A.CenterCrop(p=1, height=original_height, width=original_width)
augmented = aug(image=image_padded, mask=mask_padded)
image_center_cropped = augmented["image"]
mask_center_cropped = augmented["mask"]
print(image_center_cropped.shape, mask_center_cropped.shape)
assert (image - image_center_cropped).sum() == 0
assert (mask - mask_center_cropped).sum() == 0
visualize(image_padded, mask_padded, original_image=image_center_cropped, original_mask=mask_center_cropped)
(101, 101, 3) (101, 101)
No code provided
No code providedx_min = (128 - original_width) // 2
y_min = (128 - original_height) // 2
x_max = x_min + original_width
y_max = y_min + original_height
aug = A.Crop(x_min=x_min, x_max=x_max, y_min=y_min, y_max=y_max, p=1)
augmented = aug(image=image_padded, mask=mask_padded)
image_cropped = augmented["image"]
mask_cropped = augmented["mask"]
print(image_cropped.shape, mask_cropped.shape)
assert (image - image_cropped).sum() == 0
assert (mask - mask_cropped).sum() == 0
visualize(image_cropped, mask_cropped, original_image=image_padded, original_mask=mask_padded)
(101, 101, 3) (101, 101)
No code provided
No code providedNon destructive transformations. Dehidral group D4
For images for which there is no clear notion of top like this one, satellite and aerial imagery or medical imagery is typically a good idea to add transformations that do not add or lose the information.
There are eight distinct ways to represent the same square on the plane.
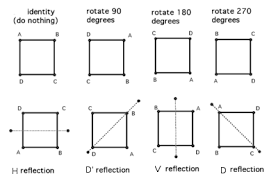
Combinations of the transformations HorizontalFlip, VerticalFlip, Transpose, RandomRotate90 will be able to get the original image to all eight states.
HorizontalFlip
aug = A.HorizontalFlip(p=1)
augmented = aug(image=image, mask=mask)
image_h_flipped = augmented["image"]
mask_h_flipped = augmented["mask"]
visualize(image_h_flipped, mask_h_flipped, original_image=image, original_mask=mask)
No code provided
No code providedVerticalFlip
aug = A.VerticalFlip(p=1)
augmented = aug(image=image, mask=mask)
image_v_flipped = augmented["image"]
mask_v_flipped = augmented["mask"]
visualize(image_v_flipped, mask_v_flipped, original_image=image, original_mask=mask)
No code provided
No code providedRandomRotate90 (Randomly rotates by 0, 90, 180, 270 degrees)
aug = A.RandomRotate90(p=1)
augmented = aug(image=image, mask=mask)
image_rot90 = augmented["image"]
mask_rot90 = augmented["mask"]
visualize(image_rot90, mask_rot90, original_image=image, original_mask=mask)
No code provided
No code providedTranspose (switch X and Y axis)
aug = A.Transpose(p=1)
augmented = aug(image=image, mask=mask)
image_transposed = augmented["image"]
mask_transposed = augmented["mask"]
visualize(image_transposed, mask_transposed, original_image=image, original_mask=mask)
No code provided
No code providedNon-rigid transformations: ElasticTransform, GridDistortion, OpticalDistortion
In medical imaging problems, non-rigid transformations help to augment the data. It is unclear if they will help with this problem, but let's look at them. We will consider ElasticTransform, GridDistortion, OpticalDistortion.
We fix the random seed for visualization purposes, so the augmentation will always produce the same result. In a real computer vision pipeline, you shouldn't fix the random seed before applying a transform to the image because, in that case, the pipeline will always output the same image. The purpose of image augmentation is to use different transformations each time.
ElasticTransform
aug = A.ElasticTransform(p=1, alpha=120, sigma=120 * 0.05, alpha_affine=120 * 0.03)
aug.set_random_seed(137)
augmented = aug(image=image, mask=mask)
image_elastic = augmented["image"]
mask_elastic = augmented["mask"]
visualize(image_elastic, mask_elastic, original_image=image, original_mask=mask)
/var/folders/68/k137nch11m76w1plfrw320r00000gn/T/ipykernel_46946/2210725196.py:1: UserWarning: Argument(s) 'alpha_affine' are not valid for transform ElasticTransform
aug = A.ElasticTransform(p=1, alpha=120, sigma=120 * 0.05, alpha_affine=120 * 0.03)
No code provided
No code providedGridDistortion
aug = A.GridDistortion(p=1)
aug.set_random_seed(137)
augmented = aug(image=image, mask=mask)
image_grid = augmented["image"]
mask_grid = augmented["mask"]
visualize(image_grid, mask_grid, original_image=image, original_mask=mask)
No code provided
No code providedOpticalDistortion
aug = A.OpticalDistortion(distort_limit=2, shift_limit=0.5, p=1)
aug.set_random_seed(137)
augmented = aug(image=image, mask=mask)
image_optical = augmented["image"]
mask_optical = augmented["mask"]
visualize(image_optical, mask_optical, original_image=image, original_mask=mask)
/var/folders/68/k137nch11m76w1plfrw320r00000gn/T/ipykernel_46946/2850517686.py:1: UserWarning: Argument(s) 'shift_limit' are not valid for transform OpticalDistortion
aug = A.OpticalDistortion(distort_limit=2, shift_limit=0.5, p=1)
No code provided
No code providedRandomSizedCrop
One may combine RandomCrop and RandomScale but there is a transformation RandomSizedCrop that allows to combine them into one transformation.
aug = A.RandomSizedCrop(min_max_height=(50, 101), size=(original_height, original_width), p=1)
aug.set_random_seed(137)
augmented = aug(image=image, mask=mask)
image_scaled = augmented["image"]
mask_scaled = augmented["mask"]
visualize(image_scaled, mask_scaled, original_image=image, original_mask=mask)
No code provided
No code providedLet's try to combine different transformations
Light non-destructive augmentations.
aug = A.Compose(
[A.VerticalFlip(p=0.5), A.RandomRotate90(p=0.5)],
seed=137,
strict=True,
)
augmented = aug(image=image, mask=mask)
image_light = augmented["image"]
mask_light = augmented["mask"]
visualize(image_light, mask_light, original_image=image, original_mask=mask)
No code provided
No code providedLet's add non rigid transformations and RandomSizedCrop
Medium augmentations
aug = A.Compose(
[
A.OneOf(
[
A.RandomSizedCrop(min_max_height=(50, 101), size=(original_height, original_width), p=0.5),
A.PadIfNeeded(min_height=original_height, min_width=original_width, p=0.5),
],
p=1,
),
A.D4(p=1),
A.OneOf(
[
A.ElasticTransform(p=0.5, alpha=120, sigma=120 * 0.05),
A.GridDistortion(p=0.5),
A.OpticalDistortion(distort_limit=1, p=1),
],
p=1,
),
],
seed=137,
strict=True,
)
augmented = aug(image=image, mask=mask)
image_medium = augmented["image"]
mask_medium = augmented["mask"]
visualize(image_medium, mask_medium, original_image=image, original_mask=mask)
No code provided
No code providedLet's add non-spatial stransformations.
Many non-spatial transformations like CLAHE, RandomBrightness, RandomContrast, RandomGamma can be also added. They will be applied only to the image and not the mask.
aug = A.Compose(
[
A.OneOf(
[
A.RandomSizedCrop(min_max_height=(50, 101), size=(original_height, original_width), p=0.5),
A.PadIfNeeded(min_height=original_height, min_width=original_width, p=0.5),
],
p=1,
),
A.D4(p=1),
A.OneOf(
[
A.ElasticTransform(alpha=120, sigma=120 * 0.05, p=0.5),
A.GridDistortion(p=0.5),
A.OpticalDistortion(distort_limit=2, p=1),
],
p=0.8,
),
A.CLAHE(p=0.8),
A.RandomBrightnessContrast(p=0.8),
A.RandomGamma(p=0.8),
],
seed=137,
strict=True,
)
augmented = aug(image=image, mask=mask)
image_heavy = augmented["image"]
mask_heavy = augmented["mask"]
visualize(image_heavy, mask_heavy, original_image=image, original_mask=mask)
No code provided
No code provided